

We all adore the sight of our furry friends panting, tongues lolling out in playful exhaustion after a spirited game of fetch or on a warm, sunny afternoon. But have you ever stopped to wonder about the deeper meaning behind this seemingly simple act? What does it tell us about our dog's health and well-being?
While we may find dog panting endearing, it serves a far more crucial purpose than just a cute quirk. Panting is an essential element of canine physiology, playing a vital role in regulating body temperature and communicating emotional states. Knowing the different types of dog panting and their underlying causes can be crucial in providing the best care for our beloved companions.
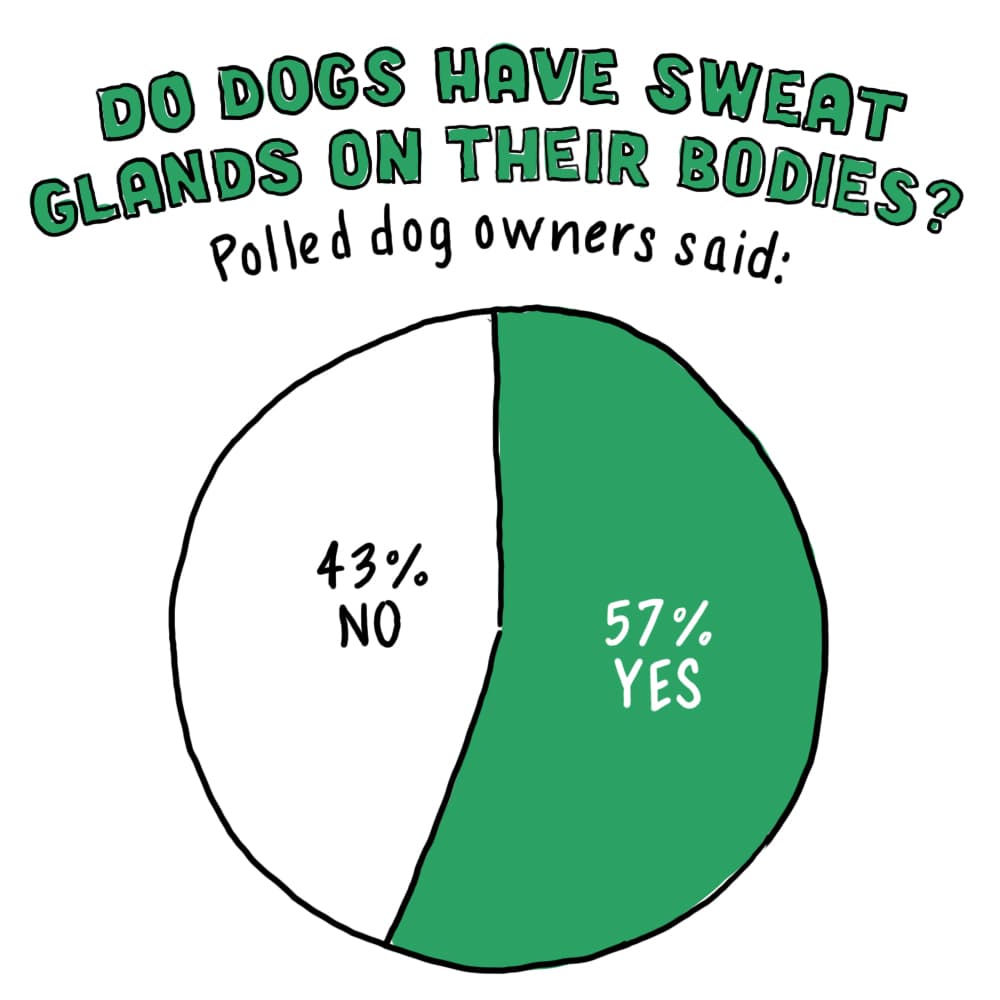
Dogs pant to regulate their body temperature, a mechanism similar to how humans sweat. While some panting is normal, excessive or unusual panting can be a sign of an underlying health issue.
Understanding why your dog pants is crucial for their health and well-being. While we've previously discussed how panting is their primary cooling mechanism, there's more to the story than just regulating body temperature.
Seeing your beloved furry friend struggling to breathe can be a harrowing experience. But before jumping to conclusions, it's important to stay calm and assess the situation. Here's what you can do when your dog is panting heavily:
If any of these factors are present, the panting is likely a normal physiological response to regulate their body temperature or manage stress. In this case, simply provide your dog with a cool, quiet space, offer fresh water, and allow them to rest.
Pay close attention to any deviations from their normal breathing patterns. Excessive panting in dogs, especially at rest or in a cool environment, may indicate an underlying medical condition and warrants further investigation.
These initial steps can help alleviate panting caused by heat or stress.
While dogs naturally pant for various reasons, like regulating their body temperature or expressing excitement, excessive or unusual panting can be a sign of an underlying health issue. Knowing when to seek veterinary attention is crucial to ensure your furry friend's well-being.
Here's when you should be concerned about your dog's panting:
Panting is a natural and essential part of a dog's physiology, but it's crucial to differentiate between normal panting and signs of distress. By understanding the reasons behind your dog's panting and knowing when to seek help, you can ensure they live a happy, healthy life.
Dogs pant primarily to regulate their body temperature. Since they can't sweat through their skin like humans, they release heat by panting, which involves rapid breathing that helps to cool their body.
If your dog is breathing fast while resting, it could be a sign of distress or an underlying health issue. Normal panting is usually seen after exercise or in hot weather, but fast breathing at rest might indicate a problem and should be checked by a vet.
Concern arises when panting is excessive, continuous, or happens during rest. Look for accompanying signs like lethargy, reluctance to move or eat, and changes in gum colour. In such cases, it's best to consult a veterinarian.


Most humans recognise a hug as a sign of affection and close friendship. That is exactly why we feel this strong urge to hug dogs out of love. After all, they are the best type of best friends. As pet parents, we love greeting our pawsome pals with dog hugs. However, do dogs like hugs? In an IAMS™ survey*, 83% of dog parents say their dog likes hugs too. Is this true? We’re going to try and get an answer to this question.
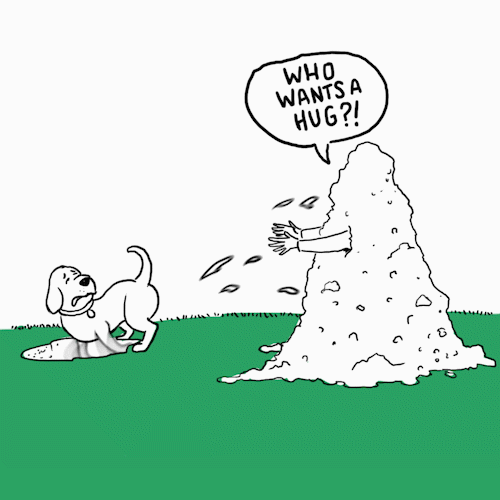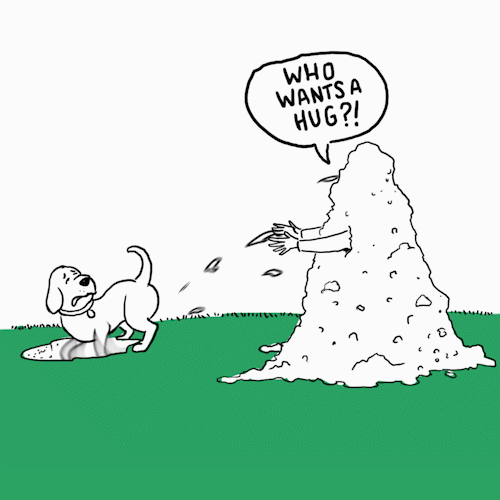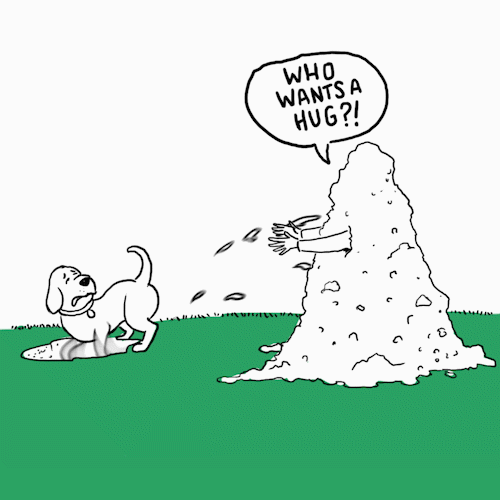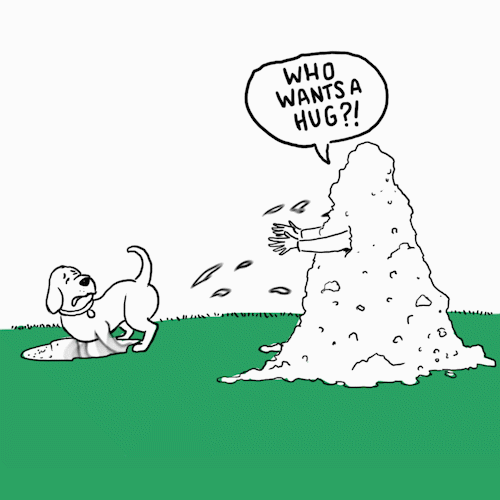
The short answer is no. Dogs do not like hugs. Now, let’s look at a bit of an explanation to this.
Some dogs enjoy canine cuddles, but usually only with their owner or household members. Otherwise, they don’t care about it. “Hugging is too much and overwhelming for many dogs and should be discouraged if the dog doesn’t know the individual very well”, advises James Serpell, B.Sc., Ph.D., Professor of Humane Ethics & Animal Welfare at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine.
So, why don’t dogs like hugs? To understand this, we may need to look at what a dog really feels when you try to hug it.
Here is what your pooch probably experiences when you try to engulf it in an embrace:
Hugging is human behaviour and not dog behaviour. These animals are just not physically built for that kind of interaction. We stand upright, so we face people. Dogs are on all fours, making hugging an unnatural act for them. Hence, they prefer a friendly sniff.
As humans, hugging your dog might seem like the purest way of expressing love, however, to dogs, a hug comes off as dominating behaviour. It feels like someone is trying to assert control over them. It can be stressful, especially if done by a stranger.
Since ancient times, a canine’s first instinctive defense has been to run away from danger. And hugging makes them feel trapped and confined. As humans, we too feel awkward when a person we barely know gives us a long and tight hug, right? Dogs somewhat feel the same. To some extent, they would also want to escape.

Sniffing is a dog’s way of expressing love. However, we humans definitely don’t regard sniffing the same way. And no matter how much we love our canine companion, we do feel a little uncomfortable with this gesture. Similarly, your pet might find hugs discomforting. Don’t worry. A dog’s body language will give you all the signs you need to know about their comfort level. But in order to understand these signs, you must learn to read them. So, let us understand some signs that indicate your dog is uneasy.
Dogs try to avoid anything that stresses them out. So, if your dog looks away when you enfold them in your arms, they don't like hugs. Your furry friend might also open their eyes wide while looking away and this allows you to notice their whale eyes. Whale eyes are when you see the whites of a dog’s eyes. Now, that is another indication of stress and discomfort.
Dogs are generally flexible when relaxed. If your dog gets stiff when you wrap your hands around them, you should probably set them free. Your dog might also lower or tuck their tail under the belly out of stress. Moreover, you must also pay attention to your pet’s ears. Lowered ears are a sign of a stressed dog.
It’s no news that we yawn when exhausted. However, if your pooch yawns during dog hugs, they are getting stressed out. It is their way of conveying that they don’t like something.
Every dog is unique. While most of them feel uncomfortable with hugs, some might like being embraced. Here’s how you can confirm if your furball doesn’t feel suffocated when you hug them:
Tail wagging can mean several things. However, you know your dog is happy when they give you a full-body tail wag. Slow, relaxed wags mean that your dog feels composed and at ease.
Placing the paws on the hugger signifies that your dog welcomes this form of attention. A dog’s paws can do more than just walk and dig holes. It is one of the most effective modes of communication for them.
Don’t worry if your dog doesn’t want to hug it out. There are plenty of healthier ways you can show them you are still their best friend: