
We all adore the sight of our furry friends panting, tongues lolling out in playful exhaustion after a spirited game of fetch or on a warm, sunny afternoon. But have you ever stopped to wonder about the deeper meaning behind this seemingly simple act? What does it tell us about our dog's health and well-being?
While we may find dog panting endearing, it serves a far more crucial purpose than just a cute quirk. Panting is an essential element of canine physiology, playing a vital role in regulating body temperature and communicating emotional states. Knowing the different types of dog panting and their underlying causes can be crucial in providing the best care for our beloved companions.
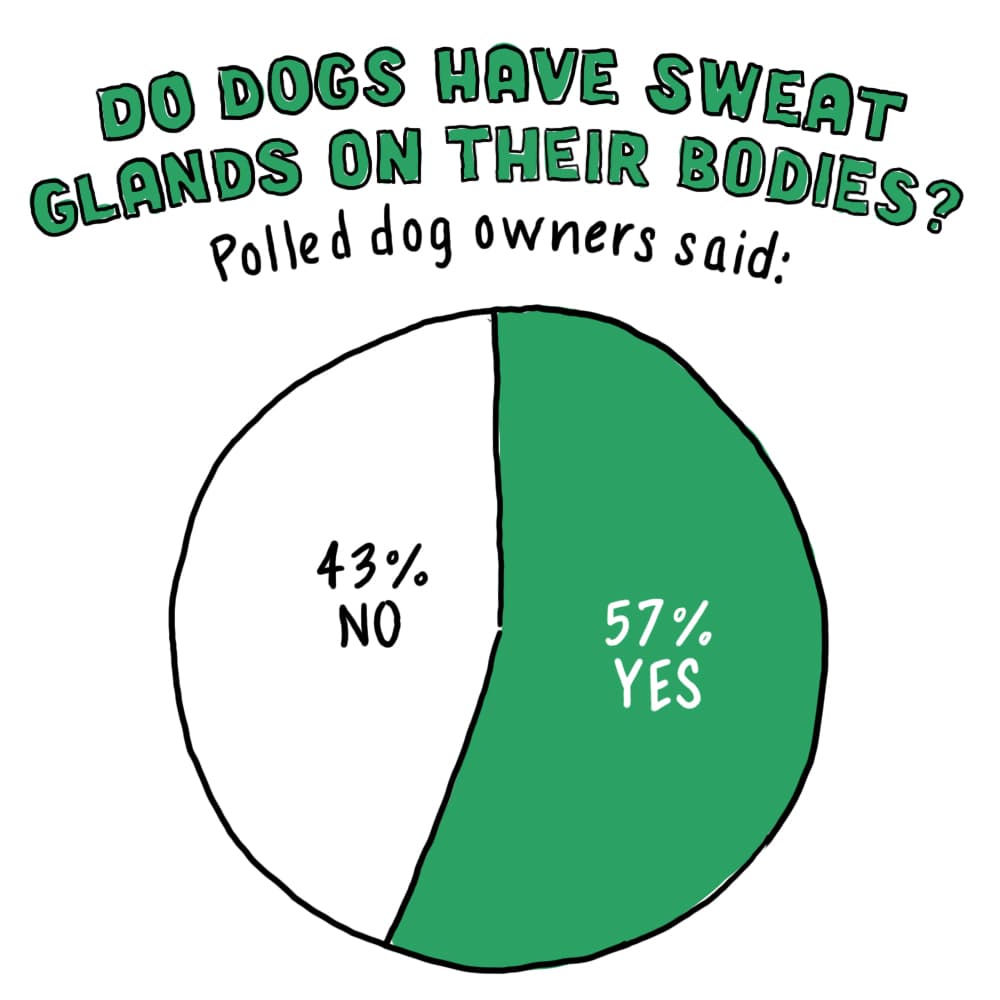
Dogs pant to regulate their body temperature, a mechanism similar to how humans sweat. While some panting is normal, excessive or unusual panting can be a sign of an underlying health issue.
Understanding why your dog pants is crucial for their health and well-being. While we've previously discussed how panting is their primary cooling mechanism, there's more to the story than just regulating body temperature.
Seeing your beloved furry friend struggling to breathe can be a harrowing experience. But before jumping to conclusions, it's important to stay calm and assess the situation. Here's what you can do when your dog is panting heavily:
If any of these factors are present, the panting is likely a normal physiological response to regulate their body temperature or manage stress. In this case, simply provide your dog with a cool, quiet space, offer fresh water, and allow them to rest.
Pay close attention to any deviations from their normal breathing patterns. Excessive panting in dogs, especially at rest or in a cool environment, may indicate an underlying medical condition and warrants further investigation.
These initial steps can help alleviate panting caused by heat or stress.
While dogs naturally pant for various reasons, like regulating their body temperature or expressing excitement, excessive or unusual panting can be a sign of an underlying health issue. Knowing when to seek veterinary attention is crucial to ensure your furry friend's well-being.
Here's when you should be concerned about your dog's panting:
Panting is a natural and essential part of a dog's physiology, but it's crucial to differentiate between normal panting and signs of distress. By understanding the reasons behind your dog's panting and knowing when to seek help, you can ensure they live a happy, healthy life.
Dogs pant primarily to regulate their body temperature. Since they can't sweat through their skin like humans, they release heat by panting, which involves rapid breathing that helps to cool their body.
If your dog is breathing fast while resting, it could be a sign of distress or an underlying health issue. Normal panting is usually seen after exercise or in hot weather, but fast breathing at rest might indicate a problem and should be checked by a vet.
Concern arises when panting is excessive, continuous, or happens during rest. Look for accompanying signs like lethargy, reluctance to move or eat, and changes in gum colour. In such cases, it's best to consult a veterinarian.


Keeping your puppy’s skin and coat healthy is as easy as 1-2-omega-3. Feeding studies have shown that dogs thrive on high-quality animal proteins from chicken, fish, lamb and eggs. IAMS™ ProActive Health™ Smart Puppy Original and other IAMS formulas are made with these highly digestible proteins, which promote excellent skin and coat condition and enhance your dog’s overall health and well-being. When your dog’s coat looks good, the rest of his body will likely be well nourished, too.
Learn more about two important nutrients that can maintain your puppy’s skin and coat health.
Fat plays a key role in keeping your puppy’s skin and coat in top condition. Fat not only provides energy, but it’s also a source of essential fatty acids that are necessary for the skin’s healthy structure. Fatty acids in the diet keep the skin moist and supple. They also contribute to a thick, lustrous and healthy coat. The lack of or imbalance of fatty acids can cause dry, scaly skin and brittle hair. A diet with vitamin-rich fish oils is vital to your puppy’s coat health and appearance.
Although there are many kinds of fatty acids, a few are important to coat health and appearance:
An appropriate balance of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids helps maintain your dog’s healthy skin and coat. An optimal range of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty-acid ratios is between 5:1 and 10:1 to enhance skin and coat quality and help nutritionally manage skin and coat conditions.
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is a key nutrient found naturally in breast milk and is important for a baby’s neural development. And just like a baby, a puppy’s ability to learn depends on healthy brain development.
At 6 weeks, a puppy's brain mass is approximately 70% developed. At this stage and in the months ahead, feeding your puppy a diet rich in DHA can help support neural development. Premium puppy foods such as IAMS™ ProActive Health™ Smart Puppy provide DHA in their formulas.
