Between 25 and 40% of dogs are overweight, but often, owners don't know it until they take their dog to the veterinarian for another reason. Yet, even veterinarians can't tell if a dog is fat just by its weight. Ideal weight varies by breed, and quite widely within breeds. There's no ideal weight chart for all dogs!
You can judge your dog's condition by placing your hands on each side of his rib cage. Are the ribs protruding? Your dog may be too thin. Can you feel individual ribs easily, and is your dog's abdomen slightly tucked up when viewed from the side? That's the sign of ideal weight. If you can't feel the ribs easily, your dog has no waist, and his abdomen drags, he's too fat. Your veterinarian can help you further evaluate your dog's weight.
Before beginning any weight loss program with your dog, discuss it with your veterinarian.
You can begin your dog's weight-loss program by reducing caloric intake by 25% of his maintenance intake, and then decrease it by 10% increments every two to three weeks until a 1% weight loss per week is achieved. This means that, if your dog weighs 15 pounds, a 1% loss would be about 2-1/2 ounces.
If you feed one large meal a day or keep food available at all times, try dividing the daily ration into several small meals (at least two meals a day) and pick up what has not been eaten 30 minutes after each meal.
Dogs gain weight for the same reason that people do—they eat more calories than they use. Today's dogs share another problem with their parents: lack of activity. Most parents are gone all day and come home too tired to play with the dog.
Also, as dogs age, or after they are spayed or neutered, their metabolism might slow causing them to require less food.
Another reason for weight gain is frequent, high-calorie treats. Sometimes, more than one family member is feeding the dog, and the dog sure isn't telling!
Losing weight isn't easy. Changing habits is the key. Here are some ways you can help:
Determine who feeds the dog what and when. (Don't be embarrassed to admit you give your dog treats. Dogs are expert beggars.)
Substitute affection for treats. Give a pat or throw a ball when he noses your hand.
Take your dog for a walk more often. Even 10 minutes a day can help.
Feed him more often. It takes energy to digest food. Dividing your dog's daily ration into two or three feedings will help.
Reducing your dog's regular food amount by 25% should bring results.
If your dog is more than 15% overweight, your veterinarian might recommend a special food. Diet foods should be low in fat (under 20% of calories from fat).
Your goal is to help your dog be healthier, so select his food carefully. Some diet foods just add fiber to help the dog feel full. This can result in reduced digestibility, large stool volume, frequent trips to the backyard, and decreased skin and coat condition because the dog isn't getting enough fat and nutrients.
Find a food, such as IAMS™ ProActive Health™ Adult Healthy Weight, that has normal fiber levels to keep your dog's digestive system working properly. It should have high-quality protein so your dog doesn't lose muscle tone and essential fatty acids to help keep his skin flexible and coat glossy throughout the dieting process. After your dog reaches ideal weight, select a maintenance food to keep weight steady.
Obesity is a common problem in dogs. Identifying the causes and following a total weight management program can result in controlled weight loss and maintenance. A total weight management program includes evaluating your dog, then modifying behaviors and successful dog weight control.
Definition of obesity
Obesity is defined as an increase in body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, resulting from an accumulation of excess body fat.
Causes of obesity
Obesity is caused when caloric intake exceeds caloric expenditure. This simply means that a dog eats more energy (calories) than he uses and stores the excess energy.
Factors contributing to obesity
Fat and carbohydrates
Dogs use fat as their primary energy source. An overweight dog stores fat more easily if the calories are consumed in the form of fat than if they are from carbohydrates. An overweight or obese dog should be fed a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet to restrict calories available from fat, which is important for dog weight control.
Fiber and fatty acids
A normal fiber level, provided in a moderately fermentable fiber source, helps create and maintain healthy digestion. This is especially important for the dog on a diet. Some weight-loss foods for dogs dilute calories with high levels of fiber. High-fiber foods may reduce the digestibility and absorption of many nutrients, including fat. These foods reduce weight by providing what would be considered poor-quality nutrition. These high-fiber diets also result in large, frequent stools and decreased skin and coat condition. Dog foods such as IAMS™ ProActive Health™ Adult Weight Control, which provide essential fatty acids like those found in vitamin-rich fish oils, help maintain your dog's healthy skin and coat despite lowered fat levels.
Gradual Weight Loss
The goal of a good weight management program should be gradual weight loss. Dogs should lose 1% to 2% of their initial weight per week. This can be achieved by reducing the caloric intake by 30% to 50% of maintenance.
A total weight management program can lead to successful weight loss in the obese dog. Before beginning any weight-loss program with your dog, discuss it with your veterinarian. Remember, your support is essential to your dog's weight-control success.


Dogs use a range of sounds to communicate with us and each other. Just as important is the body language they use to tell us how they feel or what they need. How well do you know your pooch’s unspoken cues? Read on to find out.
Dogs often stare at their owners because they love them. They want to make sure you’re okay or find clues for what you’ll do next — like making sure you’re not going for a car ride without them.
We love it when dogs do this, too, which has led to this trait being even more prominent.
Opens a new windowDr. James Serpell, BSc, PhD, Professor of Humane Ethics & Animal Welfare at University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine, explains: “We've selected dogs for this behavior. Humans love that dogs look up at them in admiration, intense loyalty. One frequent observation researchers have made is that people who handle wild dogs ... they don't look their handlers in the eye like domesticated dogs do.”
Dogs have great hearing. High-frequency sounds that humans can’t hear are especially interesting to them. Head-tilting helps them track down the source. Owners find these head tilts super cute and often reward this behavior, which, of course, makes them do it more.
Dogs yawn when they’re tired, but it’s also a possible sign they’re stressed, impatient or frustrated — like when they’re in the vet’s office, or when you won’t throw that ball you’re holding already!
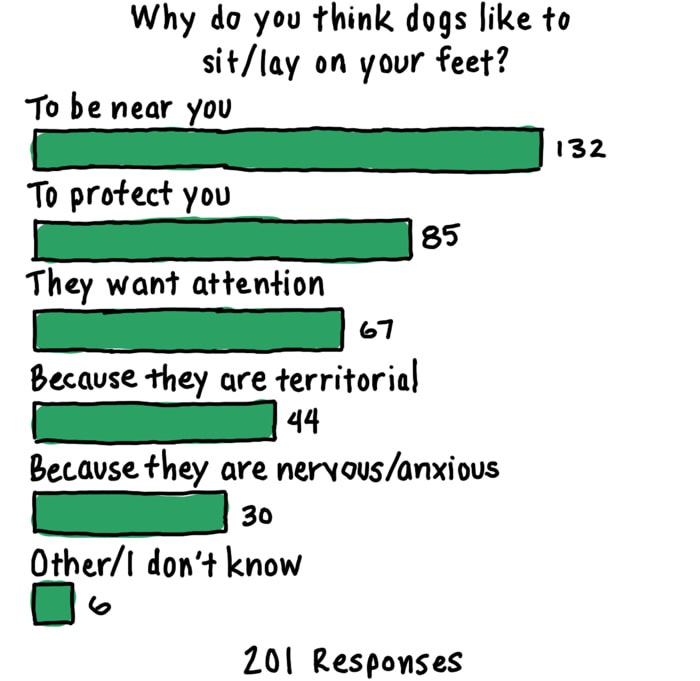
In a recent IAMS poll,* 90% of dog owners said their pet sits or lays on their feet and 100% of dogs said they love their owners. Dogs are very social creatures and this is a way for them to connect and be close to you. Plus, it keeps your feet warm.
Often called “raised hackles,” dogs do this when they’re nervous, threatened or showing aggression. It’s an adaptation from their wild days of attempting to make themselves look bigger.
Opens a new window Dr. Tammie King, Applied Behavior Technical Leader at Waltham Petcare Science Institute, offered this insight to keep in mind: “What’s important when talking about a dog’s body language is to not take one thing in isolation. You’re at risk of misinterpreting what the dog is trying to say to you. Context is everything.”
So be sure to pay attention to what your dog isn’t saying to keep them healthy and happy. Serving them
Opens a new windowIAMS dog food every day will certainly help.
*Surveyed U.S. dog owners, age 18+
Sample Size: n=201
Fielded May 8 to May 10, 2020